Understanding Bismaleimide Triazine for PCB Applications
Bismaleimide triazine resin is special in printed circuit boards. It can handle high heat and does not let electricity pass easily. The bismaleimide-triazine market is growing around the world. This is because new electronics need better materials. BT epoxy is trusted for making pcbs. It works well and is strong. It has a glass transition temperature of 180 °C. It also stays stable when it gets hot.
Property
Value
Glass Transition
180 °C
Dielectric Const.
3.70 (1 GHz)
Key Takeaways
BT epoxy resin is special because it can handle high heat and is very strong. This makes it great for printed circuit boards that need to last a long time. Its low dielectric constant helps signals stay clear. It also protects PCBs from chemicals in tough places. Engineers pick BT epoxy for new electronics. It works well with small and fast circuits. It also keeps boards safe when temperatures change.
Bismaleimide Triazine in PCBs
Key Properties
Bismaleimide triazine resin is special for making PCBs. It has a unique chemical structure. This resin mixes bismaleimide and cyanate ester. The cyanate ester makes a triazine ring. The bismaleimide part forms strong rings with nitrogen. When heated, this mix becomes tough and stable. Manufacturers use woven fiberglass cloth with this resin. They make BT epoxy laminates with it. These laminates are very strong and stable in heat. They also have a low dielectric constant.
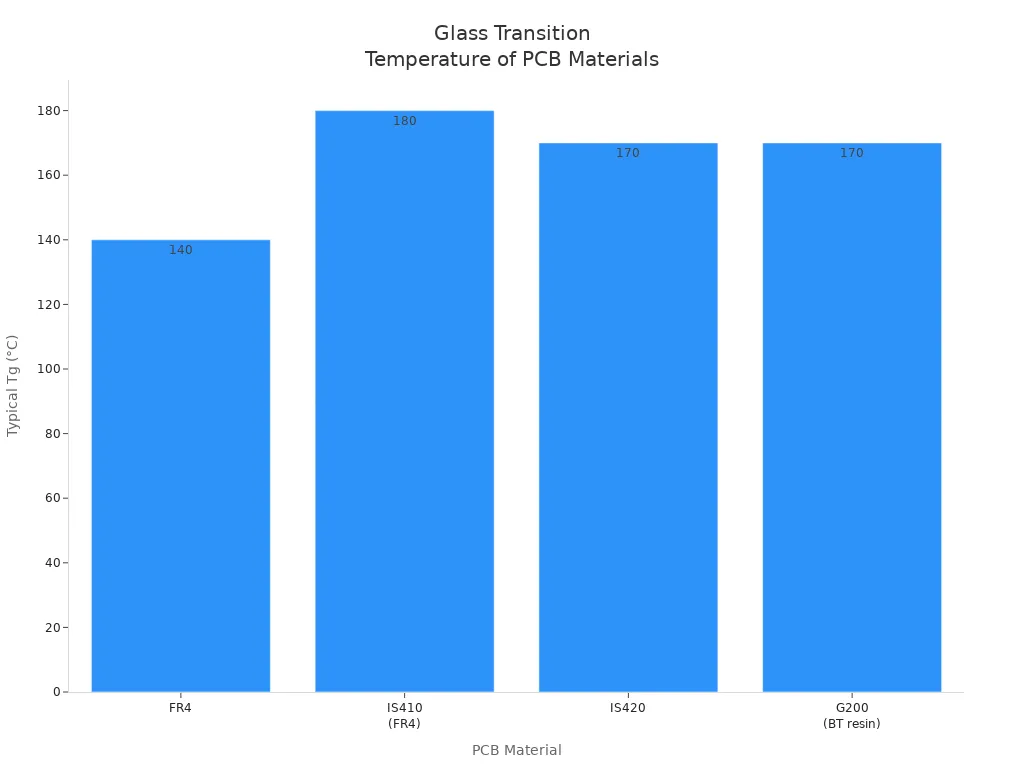
The table below shows how BT epoxy compares to other PCB materials by glass transition temperature:
PCB Material | Typical Tg (°C) | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
FR4 | ~140 | Flame retardant epoxy fiberglass composite |
IS410 (FR4) | 180 | High Tg laminate, suitable for high-temperature PCB making |
IS420 | >170 | High-performance epoxy resin with enhanced thermal properties |
G200 (BT resin based) | >170 | Epoxy and Bismaleimide/Triazine composite, high thermal resistance and strength, used in multilayer PCBs |
BT epoxy has many important features:
It can handle high temperatures, up to 180 °C or more.
It does not soak up much water, only 0.2% to 2.5%.
It has a low dielectric constant, between 2.8 and 3.5.
It keeps its shape even when heated.
These features make BT epoxy a great choice for tough PCB jobs.
Performance Benefits
BT epoxy keeps PCBs safe from heat. It helps them survive many soldering cycles and harsh places. Its high-temperature resistance stops warping and cracking. This is important during making and using the boards. The low dielectric constant helps signals move better. It reduces signal loss in fast circuits. This is needed for 5G, RF, and advanced computers.
The table below shows how BT epoxy matches up with other materials:
Property / Feature | BT Epoxy Resin Characteristics | Impact on PCB Reliability and Performance |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Stability | Resists warping and degradation during soldering | |
Dielectric Constant (Dk) | Low (3.2–3.4) | Maintains signal integrity in high-frequency circuits |
Dielectric Loss | Very low (0.003–0.004) | Ensures minimal signal degradation |
Moisture Absorption | Low | Increases durability in humid environments |
Dimensional Stability | High | Supports complex multilayer designs |
Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Prevents corrosion and material breakdown |
Strength | High mechanical strength | Withstands mechanical stress and supports miniaturization |
Note: BT epoxy does not expand much when heated or cooled. This keeps multilayer PCBs steady. This is very important for accurate and reliable electronics.
BT epoxy protects PCBs from harsh chemicals and water. This makes them last longer, even in cars, planes, and factories. Its strength helps hold tiny parts in place. This lets engineers make smaller and stronger devices.
BT epoxy also helps stop signal delay and crosstalk in fast circuits. Its great electrical performance is good for telecom, medical, and consumer electronics. Because it is strong, stable, and resists chemicals, BT epoxy is perfect for modern electronics.
BT Epoxy Applications and Comparisons
PCB Uses
BT epoxy is very important in making advanced PCBs. Companies use it for many high-performance jobs. It is often used in flip-chip ball grid array (FC BGA) and flip-chip chip-scale package (FC CSP) substrates. These packaging types help make devices smaller and faster. BT epoxy is also found in mobile devices, consumer electronics, IT, and telecom. The table below lists the main uses and their market ranks:
Application Type | Description | Market Share Rank | Growth Rate | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
FC BGA | Uses BT epoxy resin instead of ceramic; offers shorter electrical pathways and improved performance | Largest | Reduced cost, higher electrical conductivity, faster performance | |
FC CSP | Space-efficient packaging favored in smartphones and wearables | Second largest | Not specified | Demand from mobile devices, smart wearables, advanced silicon nodes |
Mobile & Consumer Electronics | Dominant application sector for BT epoxy substrates | Largest | 6.8% CAGR | Smart device adoption, 5G, AI, HPC technologies |
IT & Telecom | Second largest application sector | Second largest | Not specified | 5G infrastructure, data centers, IoT growth |
BT epoxy helps with high-density interconnect (HDI PCB) and advanced packaging. It keeps out water and keeps its shape well. It also stops electricity from leaking. These things are important for portable electronics and reliable modules. BT epoxy also helps stop bending and stress when heated and cooled. This makes it good for multilayer boards and lead-free assembly.
Material Comparison
Engineers compare BT epoxy with FR4 and ABF. Each material has special features that change how it works and how much it costs. The table below shows the main differences:
Property | BT Epoxy (G10) | FR4 | ABF (Ajinomoto Build-up Film) |
|---|---|---|---|
Heat Resistance Temperature | 160-180°C (Class F) | 125-150°C (Class B) | 150-170°C |
Glass Transition Temperature | 130-140°C | 150-170°C | |
Dielectric Constant (Dk) | 3.2–3.7 | 4.2–4.8 | 3.0–3.5 |
Mechanical Strength | High | Good | Moderate |
Chemical Resistance | Superior | Good | Good |
Moisture Absorption | <0.05% | 0.10–0.20% | 0.10–0.20% |
Cost | Most expensive | Least expensive | Moderate |
Application Focus | High-reliability, HDI, advanced packaging | General PCBs, consumer electronics | HDI PCB, build-up layers |
BT epoxy can handle more heat and is stronger than FR4. It also keeps out chemicals better and does not soak up much water.
FR4 is used for most PCBs because it is cheap and works well. It meets fire safety rules but does not handle heat as well.
ABF is used for HDI PCB as a build-up film. It costs less than BT epoxy and is good for high-density designs.
BT epoxy PCBs last longer in tough jobs. They do not expand much when heated and have a high glass transition temperature. This helps stop damage from heating and cooling. BT epoxy also stops electromigration, which keeps circuits safe in high-voltage and fast uses. FR4 is fine for normal jobs but may not last as long as BT epoxy in hard places. ABF is often used with BT epoxy in multilayer boards.
Advantages and Limitations
BT epoxy has many good points for making PCBs:
Thermal and Electrical Performance:
It can handle high heat (180°C) and breaks down at 325°C.
It has a low dielectric constant (3.2–3.7) and low loss (0.014), which helps signals stay strong.
It insulates electricity well and can handle high voltage (1200 V/mil).
It moves heat away well with a thermal conductivity of 0.35 W/m·K.
Strength and Durability:
It is very strong and helps make small, complex boards.
It keeps out chemicals and water (<0.05%), so it works well in tough places.
It keeps its shape and does not bend much when heated or cooled.
Reliability:
It does not expand much, so copper parts do not break.
It stops electromigration, which keeps circuits working in advanced packaging.
💡 Tip: BT epoxy is best for HDI PCB and advanced packaging when you need strong and reliable boards.
But BT epoxy also has some downsides:
Cost:
It costs more than other PCB materials. The price is high because the resin and process are special. There are fewer suppliers and it can take longer to get.
Making PCBs with BT epoxy needs careful control. Drilling must be exact and heat must be managed to avoid problems.
You must watch for signal problems and interference.
Every step needs good quality checks to make sure it works right.
Failure Mechanisms:
Common problems are wire bonds breaking, metal mixing, layers coming apart, and solder joints getting tired. These happen from heat and stress during temperature changes.
Innovations and Modifications
Makers keep making BT epoxy better by adding new things and mixing it with other resins. These changes help it keep out water, get stronger, and work better with electricity. Some companies, like HOREXS, have new ways to make BT substrates. Their skills help make strong solutions for computers, 5G, and mobile devices.
Engineers pick bismaleimide triazine because it stays strong in heat. It also does not let electricity pass easily and keeps out water. Knowing these things helps engineers fix design problems. It also helps them pick the best material for the job. New changes in BT resin help make better electronics. These new electronics are needed in new markets that want strong and reliable devices.
FAQ
What makes BT epoxy different from FR4 in PCBs?
BT epoxy can handle more heat and water than FR4. It also lets less electricity pass through. Engineers pick BT epoxy when they need strong and dependable boards.
Can BT epoxy be used in flexible PCBs?
BT epoxy is best for hard PCBs. Flexible PCBs need stuff that bends well. BT epoxy is not bendy enough for those uses.
Why do engineers prefer BT epoxy for advanced packaging?
BT epoxy works with tiny lines and small gaps.
It stays the same shape when it gets hot.
It keeps circuits safe in fast and crowded boards.
See Also
Key Considerations When Designing Printed Circuit Boards
Exploring Multilayer PCB Uses In Various Industry Sectors
Essential Skills Needed For Multi-Layer PCB Layout Design
Critical Process Standards For Multi-Impedance Control In PCB Manufacturing
Typical PCB Design Challenges And Fixes For SMT Technology Needs
