Choosing Between Flex Rigid and Traditional PCBs for Modern Electronics
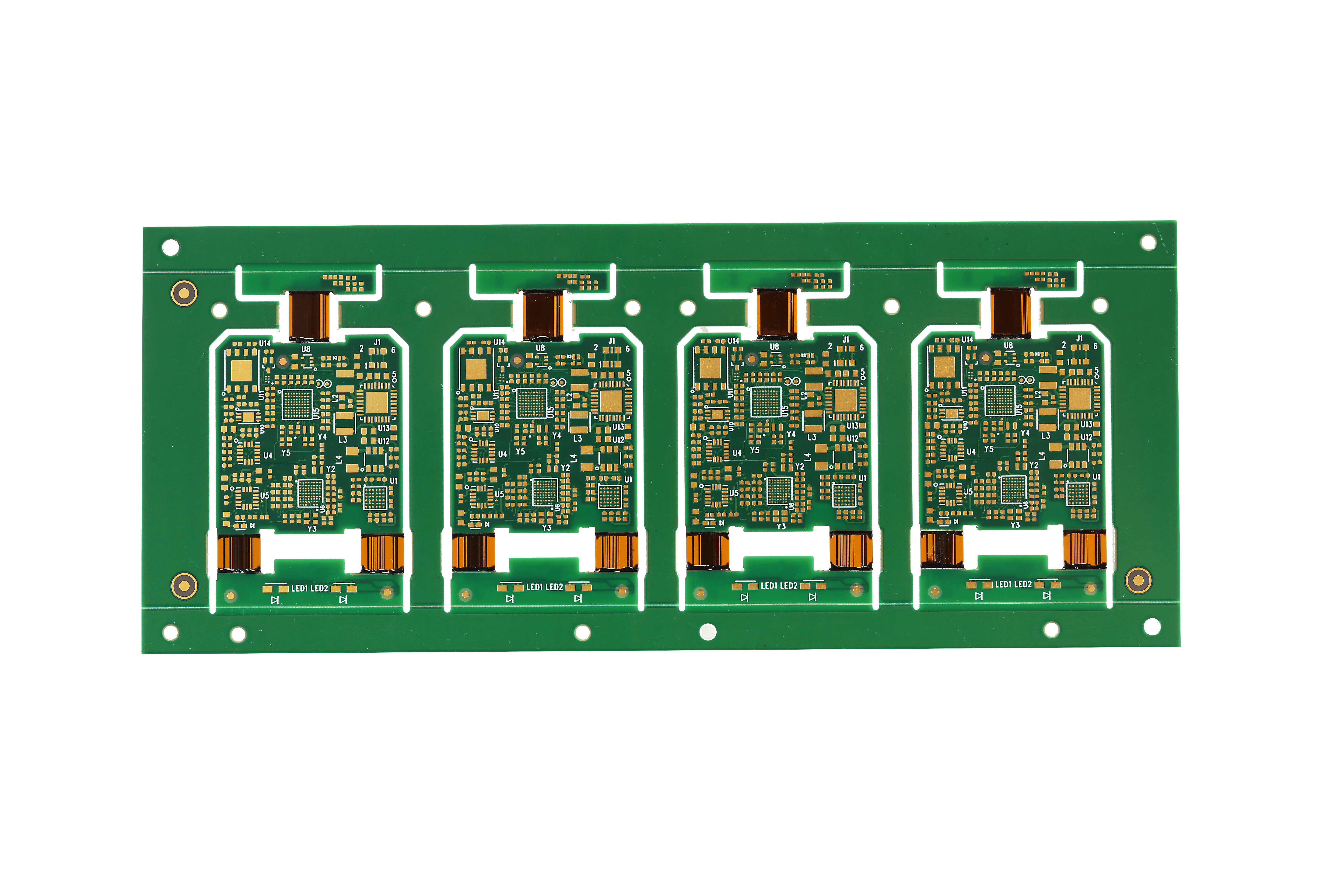
Should a designer pick flex rigid pcbs or traditional rigid pcbs for a new project? The answer depends on a few things. Important differences are cost, performance, reliability, and space needs. The table below shows how each type of printed circuit board is different:
Factor | Traditional Rigid PCBs | Flex Rigid PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Performance | Standard | Better, uses advanced materials |
Reliability | Connectors can fail | |
Application Fit | Used in small, flexible, packed designs |
Every project is different. Designers should think about these points to pick the best pcbs for their project.
Key Takeaways
Flex rigid PCBs work better and last longer in small, light, or moving devices. But they cost more than regular rigid PCBs.
Traditional rigid PCBs are cheaper and very strong. They are good for simple products that do not bend or move.
Picking the best PCB depends on your device’s size, weight, movement, and money. Careful planning helps you balance cost, quality, and how long it lasts.
Key Factors
Cost
Cost is very important when picking a printed circuit board. Traditional rigid pcbs are usually cheaper to make. They use common materials and easy steps. Flex rigid pcbs cost more at first. They need special materials and harder designs.
Here is a table that compares costs for different pcb types:
PCB Complexity | Design Cost per sq. inch | Manufacturing Cost per sq. inch | Design Time |
|---|---|---|---|
Simple 2-Layer | $0.50 - $2.00 | $0.10 - $0.50 | Low |
4-Layer | $1.00 - $3.50 | $0.20 - $0.75 | Medium |
6-Layer | $2.00 - $5.00 | $0.40 - $1.00 | Medium to High |
8+ Layer | $3.50 - $10.00+ | $0.80 - $2.00+ | High |
Designers should think about both first costs and future costs. Using fewer layers or basic materials can save money. For example, one company changed a 6-layer car pcb to a 4-layer one. The price dropped from $16 to $12 for each board. This saved 25% and the board still worked well. Long-term costs also include work, tools, and setup. Picking the right design and materials helps keep costs and quality balanced.
Performance
Performance is also very important. Flex rigid pcbs often work better in new electronics. They use materials that help fast signals and small layouts. This means less signal loss and better reliability. Traditional rigid pcbs give normal performance for simple devices.
Flex rigid pcbs are good for things like phones or medical tools. These need lots of parts close together and fast signals. Traditional rigid pcbs are fine for easy circuits and slow speeds. If you need strong signals and to save space, flex rigid pcbs are better.
Tip: More layers and special materials make boards work better but cost more. Always pick what your project really needs.
Reliability
Reliability means how long something works without breaking. Flex rigid pcbs have fewer connectors. This means there are fewer places to break. They are better for things that bend or move, like wearables or foldable phones. Traditional rigid pcbs have more connectors and are best for things that do not move.
Flex rigid pcbs can handle shaking and bending many times. This makes them great for planes, cars, and medical tools. Designers should think about how much stress the pcb will get. Picking the right type helps stop problems and keeps things working longer.
Application Fit
Application fit means picking the right pcb for the job. Each pcb type is best for certain uses. The table below shows which type fits which job:
PCB Characteristic | Options | Advantages | Typical Applications | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Layer Count | Single-sided | Low cost, simple | Remote controls, appliances | Low |
Double-sided | Moderate complexity | Consumer electronics, cars | Medium | |
Multilayer | High density, compact | Smartphones, medical devices | High | |
Substrate Material | Rigid | Durable, cost-effective | LED lighting, power devices | Low-Medium |
Flexible | Bendable, lightweight | Wearables, foldable phones | Medium-High | |
Rigid-Flex | Space-saving, reliable | Aerospace, medical devices | High |
Flex rigid pcbs are best for small, light, or moving things. Traditional rigid pcbs are good for simple and strong products. Designers should look at the size, shape, and use of the device. Picking the right pcb type gives the best mix of cost, performance, and reliability.
Flex Rigid PCBs vs. Traditional Rigid PCBs
What Are Flex Rigid PCBs?
Flex rigid pcbs mix the good parts of flexible and rigid boards. These boards have both rigid and flexible areas in one piece. The rigid parts hold the parts and make the board strong. The flexible parts link the rigid areas and let the board bend or fold. This helps designers put more electronics in small places.
A flex circuit can have as many as 20 layers. It can handle shaking and big changes in temperature, from -50°C to +125°C. The board is thin and light, so it works well in planes, medical tools, and foldable gadgets. Flex pcbs use polyimide layers and copper lines. They often have a coverlay for more safety. Making these boards needs special steps like lamination and careful checks.
Note: LT CIRCUIT makes advanced flex rigid pcbs for many fields. Their boards meet high quality and performance rules.
What Are Traditional Rigid PCBs?
Traditional rigid pcbs use a hard, stiff base. Most use FR-4, which is strong fiberglass. These boards do not bend or fold at all. They are good for things that need a flat, steady surface. Rigid boards are used in computers, TVs, and power tools.
In 2024, traditional rigid pcbs are used most in planes and defense. They are found in sensors, military robots, and power systems. These boards work well and last long in tough places. Multilayer rigid pcbs are liked for important hardware and communication gear.
A rigid circuit is made with easy steps. The process has layering, drilling, and putting on parts. The price is less than flex pcbs. For example, a double-sided rigid FR-4 pcb that is 100 × 100 mm costs about USD 0.49.
Core Differences
Flex rigid pcbs and traditional rigid pcbs are not the same in how they are built, what they are made of, and how they are used. The table below shows the main ways they are different:
Feature | Flex Rigid PCBs | Traditional Rigid PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Structure | Hybrid of rigid and flexible sections | Solid, inflexible base |
Maximum Layers | Up to 20 | Usually fewer than 12 |
Materials | Polyimide, copper, coverlay | FR-4, copper |
Weight and Thickness | Thinner, lighter | Thicker, heavier |
Manufacturing Steps | Complex lamination, special testing | Simpler, standard steps |
Cost (per 75x100mm/100x100mm) | USD 8.78 (flexible, one-sided) | USD 0.49 (rigid, double-sided) |
Vibration Resistance | High (used in moving/bending devices) | Moderate (used in stable devices) |
Operating Temperature | -50°C to +125°C or wider | Narrower range |
Typical Applications | Aerospace, medical, foldable electronics | Computers, TVs, power devices, defense |
Flex pcbs work better in small, light, or moving things. They can take shaking and work in very hot or cold places. Traditional rigid pcbs give strong support and last long in steady places. Flex circuit designs let people make creative shapes and save space.
LT CIRCUIT makes both flex rigid pcbs and traditional rigid pcbs. They know a lot about flex circuit tech and strong rigid board making. Customers can pick the best board for what they need, like high performance, bending, or saving money.
Tip: Flex pcbs and rigid flex circuits help with space and weight problems. Traditional rigid pcbs are still great for strong, simple things.
Flex PCBs in Modern Design
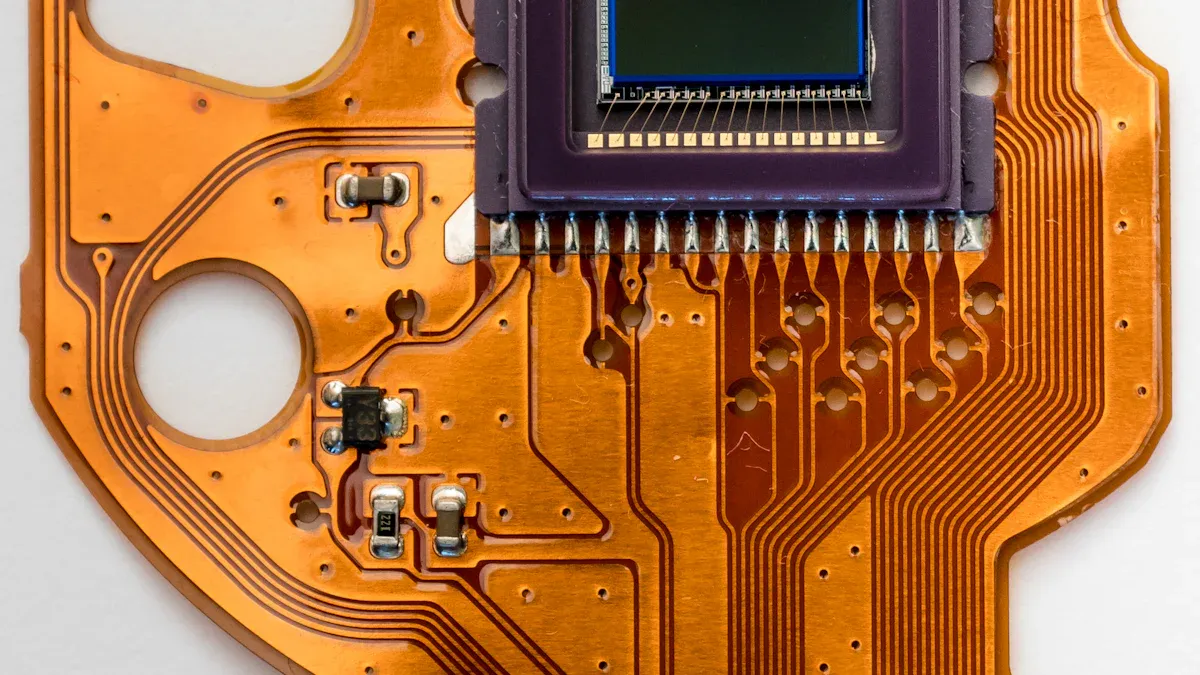
Space and Weight
Flex pcbs help engineers make smaller, lighter devices. These boards use very thin materials, sometimes only 0.004 inches thick. This thinness makes the device weigh less. Lighter devices are easier to carry and cost less to ship. Flexible pcbs can bend, fold, or roll up. This lets engineers fit more electronics into small spaces.
Many products use flex pcbs to add more features. Rigid flex circuits mix strong and bendy parts. They need fewer connectors and cables. This makes the system smaller and lighter. Fewer parts also means less chance of breaking. LT CIRCUIT uses new ways to make flexible pcbs for modern electronics. Their boards help companies build small and reliable products.
Flex circuit designs soak up shaking, which protects the device.
Rigid-flex pcbs use lighter parts, so there is more room for features.
Taking away connectors and cables makes the system even lighter.
Signal Integrity
Flex pcbs help keep signals strong in many devices. The short, straight paths in a flex circuit lower signal loss. This keeps the device working well, even when it is small. Flexible pcbs also use fewer solder joints and weak wires. This makes the board stronger and keeps signals clear.
LT CIRCUIT’s flex pcbs use good materials for fast signals. Their boards work great in things like medical tools and smartphones. By using flex pcbs, engineers make sure their products stay fast and work well.
Design & Manufacturing
Complexity
PCB design is harder now than before. Designers use many kinds of parts. They also handle lots of data. Automated tools help them keep track of everything. Teams must share data and use the same info. Good data management stops mistakes and keeps work on time. LT CIRCUIT uses smart systems to solve these problems. They make sure each pcb design is correct and ready to build.
Teams need tools to help them work together and avoid mistakes.
Keeping data in one place makes designs safe and easy to change.
Prototyping
Prototyping lets engineers test ideas before making many boards. Fast prototyping saves time and money. For example, a medical device company used early testing and modular prototypes. They found and fixed 37 problems before making the final product. This saved about $250,000 in changes. In cars, quick prototyping cut costs by 18.7% and made products better. LT CIRCUIT helps customers make prototypes fast for both flex rigid and traditional pcbs. This helps them get products out quicker and control costs.
Case Study | Results Summary |
|---|---|
Medical Device Startup | |
Automotive Electronics | 18.7% cost reduction, improved reliability |
Quality Assurance
Quality checks make sure pcbs work well and last long. Rigid-flex pcbs have fewer solder joints, so they break less. Polyimide in flex pcbs can take heat up to 400°C. Standards like IPC-6013 and IPC-2223 test for bending and heat. LT CIRCUIT uses strong tests to meet these rules. Their focus on quality and support helps customers trust their boards.
LT CIRCUIT is a leader in new ideas and quality. They give strong support from design to delivery.
Making the Choice
Assessing Needs
Every project begins by knowing what the device must do. Engineers think about the size and weight of the device. They also ask if the device will move a lot. Some devices need to bend or fit in tight spots. Flex pcbs are good for light and bendy products. Traditional pcbs are better for things that stay still and need to be strong. Good planning uses data from design tools. Automated systems help teams track changes and work together. These tools stop mistakes and make sure everyone uses the newest design. Tests like AOI and stress checks show how flex pcbs will work. This helps engineers choose the right pcb for each job.
Real-World Examples
PCB Type / Characteristics | Performance Requirements / Applications | |
|---|---|---|
Automotive | Durable flex pcbs | Must handle vibration, heat, and moisture in sensors, displays, and controls |
Aerospace | Lightweight, oxidation-resistant | Used in satellites and control towers, must survive extreme conditions |
Medical | Advanced flex pcbs and rigid-flex | Used in heart monitors and scanners, need high reliability |
Consumer Electronics | Standard and flex pcbs | Used in phones, computers, and TVs for daily use |
These examples show how engineers pick flex pcbs or traditional boards. They choose based on what each field needs. LT CIRCUIT gives custom solutions for these tough jobs.
Decision Checklist
Engineers use a checklist to pick the best pcb. They check trace width, spacing, and pad size. This helps stop shorts and makes soldering easier. They look at thermal relief to keep things cool. Mechanical rules help stop bending or breaking. Safety checks protect the device from electrical problems. Teams also check if the maker gives good support and fast delivery. They want help with debugging too. They balance cost and quality and check the parts list. This stops missing pieces. LT CIRCUIT uses these steps to help customers get the best boards for their needs.
Picking the best PCB depends on what your project needs. Here is a checklist you can use:
Look at how big and heavy the device is.
Think about if the device needs to bend.
Check how much money you can spend.
Make sure the board will last and work well.
If you want help, talk to LT CIRCUIT. Getting good advice helps you make better electronics.
FAQ
What is the main benefit of using flex rigid PCBs?
Flex rigid PCBs help save space and make things lighter. They let designers make cool shapes for small or folding gadgets.
Can traditional rigid PCBs handle high temperatures?
Traditional rigid PCBs work fine in most devices. They can take some heat but not very high heat like in space planes.
How does LT CIRCUIT support custom PCB projects?
LT CIRCUIT helps with design, quick samples, and checking quality. Their team helps customers from the first idea to the finished board.
Tip: Always tell the maker what your project needs for the best results.
See Also
Choosing Between Flexible And Rigid PCBs For Electronics
A Comprehensive Guide To The Structure Of Rigid-Flex PCBs
How Rigid-Flex PCBs Are Used In Medical And Industrial Devices
Top Benefits Of Rigid-Flex PCBs For Compact Electronic Designs
