What is a Multilayer Metal Core PCB and How Does It Work
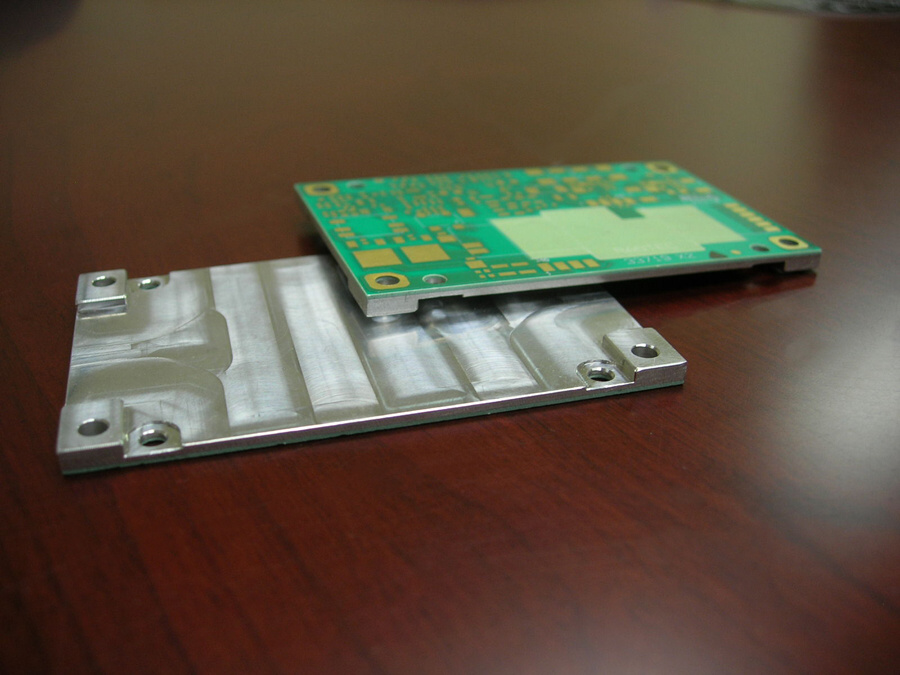

A multilayer metal core pcb features multiple PCB layers bonded together with a metal core, typically made of aluminum or copper. This construction significantly enhances heat dissipation, allowing the multilayer metal core pcb to deliver superior performance in advanced electronic applications by efficiently transferring heat away from critical components. The global market for metal core PCBs reached $4.85 billion in 2024, reflecting the growing demand for multilayer metal core pcb solutions due to their reliability and effectiveness in thermal management.
Metric/Aspect | Data/Insight |
|---|---|
Global Market Size (2024) | USD 4.85 billion |
Importance of MCPCBs | Better heat control for strong devices |
Key Takeaways
Multilayer metal core PCBs have a metal core and many layers. They move heat away fast. This helps keep devices cool and working well.
These PCBs make boards stronger and help control heat better. They last longer and give better signal quality than regular PCBs.
People use them a lot in LED lighting and cars. They are also used in electronics and other places where heat and strength are important.
Multilayer Metal Core PCB Structure

Layer Composition
A metal core pcb has many layers to help it work better. The top copper layer lets signals move around the board. Under this is a dielectric layer that keeps the copper and metal core apart. The metal core is in the middle and helps move heat away. Other layers, like ground and power planes, help control signals and power. Prepreg layers hold everything together. Vias are small holes that link the layers. This setup makes the board strong and tough. That is why metal core pcbs work well in hard places.
Description | Impact on Performance | |
|---|---|---|
Top Layer | Outermost layer with copper traces and components. | Enables signal routing and component networking. |
Signal Layers | Internal copper layers for routing signals. | Maintain signal integrity and reduce EMI. |
Ground/Power Planes | Copper planes for return paths and power distribution. | Reduce noise, improve signal integrity, and stabilize voltage. |
Dielectric Layers | Insulate conductive layers from the metal core. | Provide mechanical strength and insulation. |
Metal Core | Aluminum or copper core for heat dissipation. | Enhances thermal conductivity and mechanical support. |
Vias | Plated holes connecting layers. | Enable inter-layer connectivity. |
Metal Core Materials
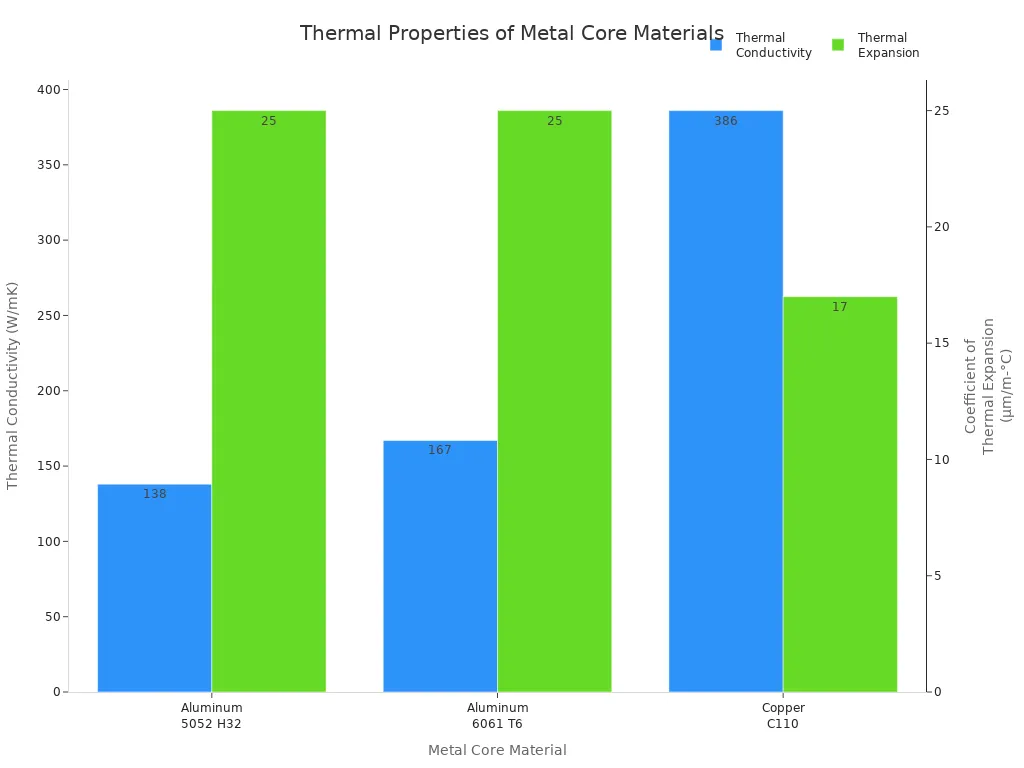
Metal core pcbs use different materials for the core. Aluminum is used most because it is light, cheap, and moves heat well. Copper moves heat even better and works well with electricity, but it is heavy and costs more. Steel alloys are not used much since they do not move heat as well. The metal core is usually between 0.76 mm and 3.2 mm thick. Thicker cores make the board stronger and help it lose heat faster. This is important for boards that use a lot of power. The dielectric layer is kept thin so heat can move through it easily. The chart below shows how well different core materials move heat and handle expansion:
LT CIRCUIT’s Approach
LT CIRCUIT uses special materials and smart designs to make their metal core pcbs better. They pick dielectrics and ceramic substrates that help high-frequency signals and move heat well. They use laser drilling to make very exact vias. This lowers mistakes and helps line up the layers. LT CIRCUIT also uses custom stack-ups and buried via technology. This lets them make smaller boards that still handle heat well. They check quality with X-rays to make sure each mcpcb is good. These steps help LT CIRCUIT make metal core pcbs that are strong, reliable, and last a long time. Their boards are used in cars, medical tools, and 5G.
How Multilayer Metal Core PCBs Work
Heat Dissipation
A multilayer metal core pcb is built to handle heat well. The copper layers help move heat sideways across the board. These copper layers are good at carrying heat fast. The metal core, made from aluminum or copper, sits in the center. It helps pull heat away from the hottest parts. Thin dielectric layers keep the copper and core apart. These layers do not block heat from reaching the core.
Thermal vias are tiny holes filled with metal. They let heat travel from the top down to the metal core. This design moves heat sideways and downward, so the board stays cool. The multilayer setup gives heat many ways to escape. This stops hot spots and keeps important parts safe.
Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
Copper layers move heat much better than FR-4. | |
Core Layer | The metal core moves heat up and down. |
Heat Diffusion | Copper spreads heat sideways, vias move it down. |
Lateral Heat Transfer | Heat also leaves through the sides of the board. |
Multilayer Structure | The board acts like two boards joined by the core. |
Designers use different tricks to help heat leave the board:
Use lots of thermal vias to move heat down.
Choose materials that carry heat well.
Make copper layers thicker for better heat spreading.
Add heat sinks or fans if needed.
A metal core pcb can move heat much faster than a regular pcb. This makes it great for things like LED lights and power tools. Good heat control keeps the board safe and helps it last longer.
Electrical Performance
A multilayer metal core pcb does more than just cool things down. It also helps signals move better through the board. The metal core pcb keeps signals strong and clear, even when they move fast. The special materials and layers help control impedance. This means signals do not bounce or get lost.
Good impedance matching means fewer mistakes in fast circuits.
Thinner cores and special dielectrics lower signal loss. For example, a 0.8 mm core can cut signal loss by 30% at 5 GHz.
Lower dielectric constant materials make signals move faster. A Dk of 3.0 can boost speed by 20% compared to a Dk of 4.5 at 10 GHz.
Good design stops crosstalk, so signals do not mix.
The multilayer metal core pcb uses these features to keep data moving fast and safe. This is important for things like 5G, computers, and medical tools. The metal core pcb also keeps the board steady, so signals do not change when it gets hot.
Advantages Over Standard PCBs
Metal core pcbs have many benefits over regular pcbs. The biggest one is better heat control. Regular pcbs cannot move heat well and often need extra heat sinks. A metal core pcb spreads and removes heat quickly, so parts do not get damaged.
Feature | Multilayer Metal Core PCBs (MCPCBs) | Standard PCBs (e.g., FR-4) |
|---|---|---|
Dimensional Change on Heating | About 2.5% to 3.5% | About 4% |
Thermal Stability | Better thermal stability, less bending | Lower thermal stability, more bending |
Mechanical Strength | Strong metal core, less likely to break | Weaker, easier to break |
Structural Integrity | Metal core keeps layers steady | No metal core, less support |
Other big advantages are:
Higher mechanical strength. The metal core makes the board tough.
Better size stability. The board changes size less when it gets hot.
Less bending and twisting. This matters for boards that get very hot.
More reliable. The strong build and good heat control help the board last longer.
A multilayer metal core pcb costs more to make than a regular pcb. But the better performance and longer life make it worth the price. Metal core pcbs are best for jobs where heat and strength are important.
Applications and Manufacturing
Industry Uses
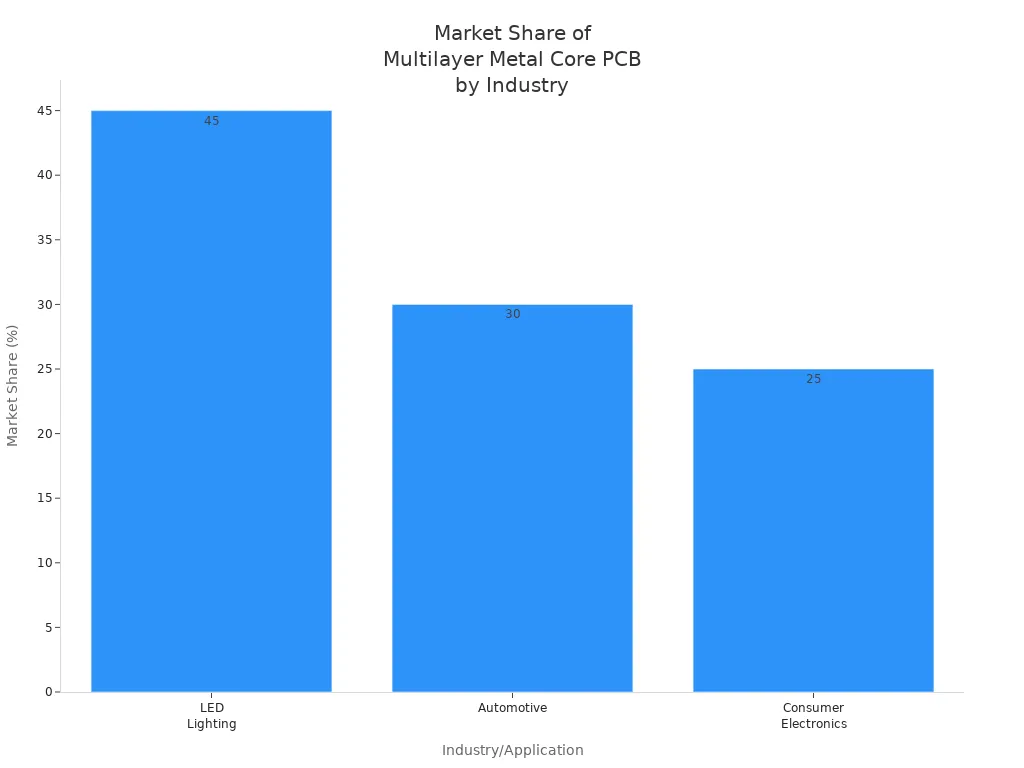
Many industries use metal core pcbs in their electronics. LED lighting is the biggest user. These boards are in street lights, tunnel lights, and flood lights. Car companies use them in LED headlights and power converters. They also use them in sensor modules. Phones and tablets use these boards because they are small and control heat well. Telecom, factories, planes, and hospitals also use metal core pcbs. They need these boards for good heat control and to work well for a long time.
Industry/Application | Market Share (%) | Key Drivers/Notes |
|---|---|---|
LED Lighting | 45 | Energy-saving lights, strong heat control. |
Automotive | 30 | Electric cars, smart driver systems. |
Consumer Electronics | 25 | Smart gadgets, small and fast boards. |
Telecommunications | N/A | Lots of circuits, needs good heat control. |
Industrial Equipment | N/A | Strong boards, moves heat in big machines. |
Aerospace & Defense | N/A | Needs to work in tough places. |
Healthcare & Medical | N/A | Small, cool-running medical devices. |
LT CIRCUIT Manufacturing Process
LT CIRCUIT uses a careful process to make these boards. First, they pick the right metal core, like aluminum or copper. This helps the board move heat away. Next, they add a special insulation layer to the core. This keeps the copper safe but lets heat pass through. They drill holes for vias and parts. Then, they coat the holes with copper to make strong links. A photoresist is put on, and extra copper is removed to make the circuit. A soldermask covers the board for safety. Labels are printed with silkscreen. The copper pads get a finish like ENIG or HASL. LT CIRCUIT checks each board with AOI, X-ray, and flying probe tests.
LT CIRCUIT uses high-tech checks and strict rules to make sure their metal core pcbs work well for tough jobs.
Key Considerations
Designers must think about heat, signals, and strength when using these boards. They use thermal vias and thick copper to move heat away from hot spots. Special stack-ups help too. The metal core makes the board strong and stops it from bending. For fast signals, they use materials with low dielectric constants. This keeps signals clear. Vias and traces are placed carefully to stop signal loss and noise. LT CIRCUIT follows rules like IPC-6012B and UL 796 to keep boards safe. Customers often want boards with 1-12 layers, thick copper, and strong insulation. These things help metal core pcbs work well in lights, cars, and power tools.
Multilayer metal core PCBs have special layers and a metal core. These help control heat and make the board work better. Many companies use these PCBs for hard jobs.
Cars and factories use these PCBs to last longer and break less.
LT CIRCUIT gives strong PCBs fast and checks their quality well.
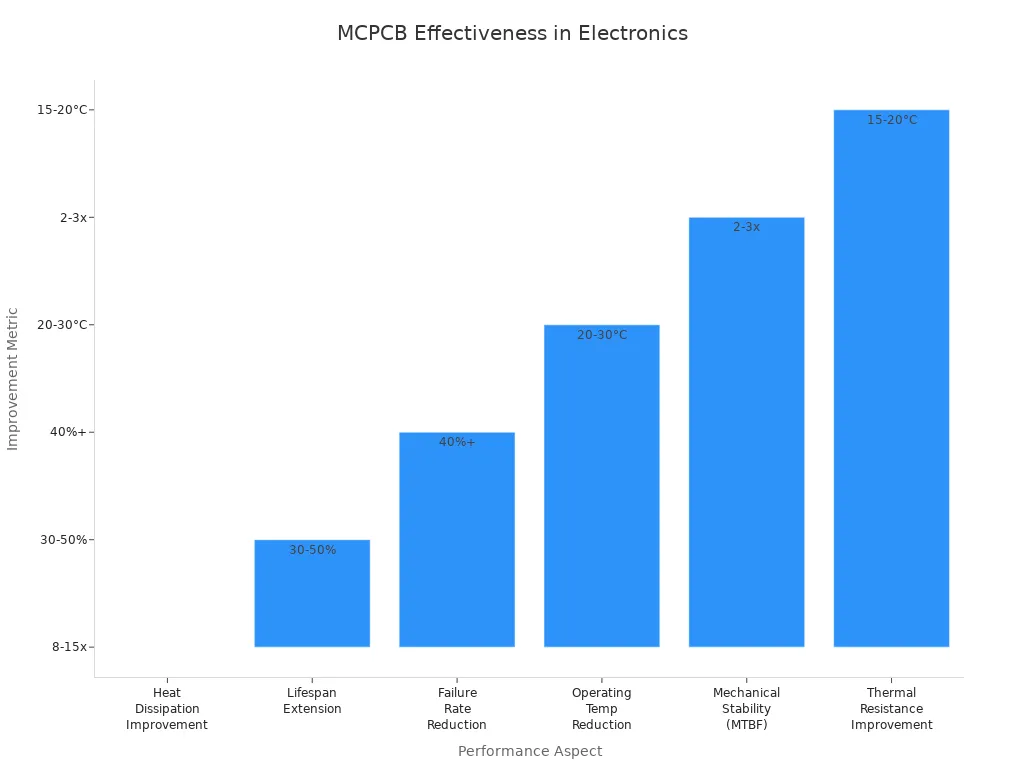
Benefit | Improvement Example |
|---|---|
Heat Dissipation | |
Lifespan | 30-50% longer for LED lighting |
Failure Rate | Over 40% reduction in power modules |
LT CIRCUIT uses smart tools and gives fast answers. This helps customers pick the best PCB for what they need.
FAQ
What makes a multilayer metal core pcb better for heat dissipation?
A multilayer metal core pcb has a metal core and special layers. This setup helps heat move away from parts quickly. It keeps devices cool and safe by managing heat well.
How does a metal core pcb improve thermal conductivity?
The metal core pcb uses aluminum or copper for the core. These metals move heat fast because they have high thermal conductivity. This helps the pcb stay cool and spread heat better.
Where do engineers use mcpcb and metal core pcbs most often?
Engineers use mcpcb and metal core pcbs in LED lighting, power electronics, and telecom. These boards work well in places with lots of heat. They help devices run safely and last longer.
See Also
Understanding Multilayer PCBs And Their Role In Electronics
Step-By-Step Guide To Manufacturing Multilayer PCBs
An Introduction To PCB Boards And Their Fundamental Principles
