Rigid Flex PCBs and their applications in industrial control and medical equipment
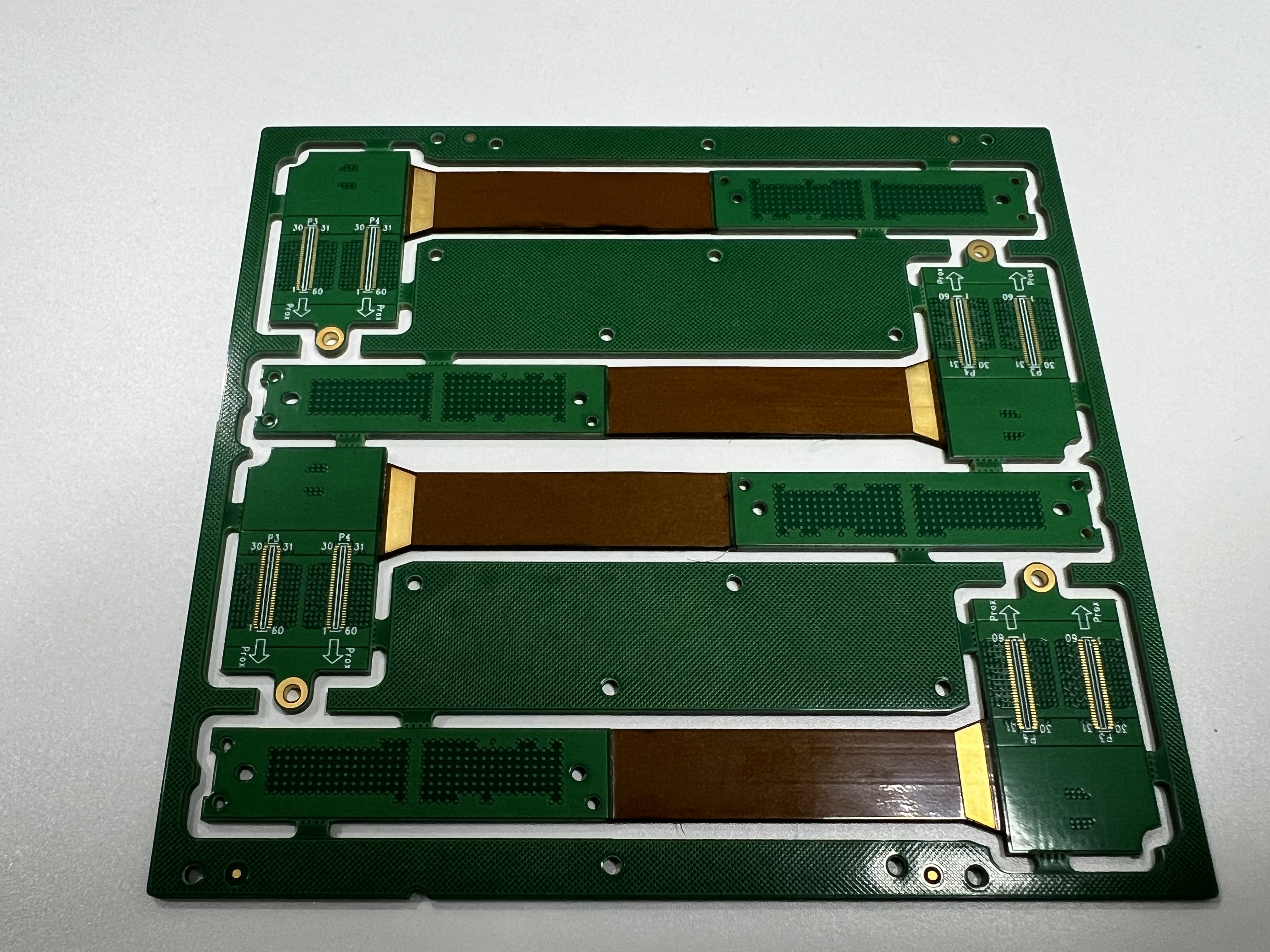
Rigid Flex PCBs combine durable rigid PCBs with flexible designs, offering a versatile solution for various applications. They play a crucial role in factory systems and medical devices. These boards are highly reliable and optimize space in critical areas. In the healthcare sector, the adoption of Rigid Flex PCBs is rapidly increasing. The medical device market is projected to grow from $0.8B in 2023 to $1.5B by 2032, driven by advancements in healthcare technology.
Key Takeaways
Rigid Flex PCBs mix stiff and bendable parts, making them great for small and tricky uses in healthcare and machines.
These boards are strong and last long, with fewer connection spots to work well in hard conditions.
More medical tools now use Rigid Flex PCBs to make smaller, better devices that help patients more.
What are Rigid Flex PCBs?
Definition and structure of rigid-flex circuit boards
Rigid-flex circuit boards mix rigid and flexible parts in one design. The rigid sections give strength, while the flexible parts can bend or fold. This mix lets engineers make small and complex designs that regular PCBs can't handle.
Rigid-flex PCBs come in different types based on layers and uses:
Type 1: One layer with a single conductive surface, good for bending.
Type 2: Two layers with holes for better connections in flexible designs.
Type 3: Three or more layers, often used for designs that don't move much.
Type 4: Combines many layers of rigid and flexible materials for tough designs.
This special design makes rigid-flex PCBs perfect for industries needing small, strong, and dependable electronics.
Key features of rigid-flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs have unique features that make them stand out:
Design flexibility: They allow creative designs with both rigid and flexible parts.
Enhanced reliability: Fewer connection points mean fewer chances of breaking.
Space efficiency: Their small size saves space, great for portable gadgets.
Durability: They resist shaking and stress, lasting longer in tough conditions.
Thermal management: Better airflow and heat control improve device performance.
These features make rigid-flex PCBs popular for medical tools, factory systems, and aerospace devices.
Differences between rigid-flex and traditional PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs are very different from regular PCBs in design and use. The table below shows these differences:
Attribute | Rigid-Flex PCBs | Traditional PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Bends in certain areas | Fully stiff |
Complexity | Very detailed designs | Simpler designs |
Reliability | Very dependable | Average dependability |
Space Efficiency | Saves lots of space | Uses more space |
Durability | Very strong | Less strong |
Applications | Medical, aerospace, defense, consumer electronics | General uses |
Rigid-flex PCBs also perform better than regular PCBs in key areas:
Enhanced signal integrity: Fewer connections mean less noise and interference.
Improved mechanical stability: They handle stress well, staying stable in tough places.
Compact design: Fewer cables and connectors make devices lighter and smaller.
By combining the best of rigid and flexible PCBs, rigid-flex designs are great for advanced technology.
Advantages of Rigid Flex PCBs
Strong and dependable for tough jobs
Rigid-flex PCBs are tough and reliable. They work well in factories and hospitals. These boards handle hard conditions without breaking. Fewer connection points mean fewer problems. This makes them great for machines and medical tools that must work all the time.
Manufacturers test these boards to prove their strength:
Test Type | What It Checks |
|---|---|
ESD/EMP Testing | Checks if the board can handle electric shocks and magnetic pulses. |
Moisture Resistance Testing | Tests if water can damage the board. |
Vibration Testing | Makes sure the board works after shaking or moving. |
Low Pressure Testing | Tests how the board works in thin air, like high places. |
Thermal Cycling Testing | Checks if the board can handle hot and cold changes. |
These tests show rigid-flex PCBs can survive tough environments. They are dependable for factory machines and medical devices.
Saves space and fits anywhere
Rigid-flex PCBs are small and save space. They mix stiff and bendable parts to fit tight spots. This is helpful for small medical tools and factory machines with little room.
They don’t need big connectors or cables. This makes devices smaller and lighter. You can make slim products that still work well. This is important for wearable medical gadgets and robots where space matters.
Works well in hard conditions
Rigid-flex PCBs are strong in extreme places. They stay steady in heat, cold, shaking, or air pressure changes. These boards keep working in factories and hospitals.
Manufacturers test them to meet high standards:
Test Type | What It Checks | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Cycling Test | Checks if the board can handle hot and cold repeatedly. | -40°F to +257°F |
Thermal Shock Test | Tests if the board can survive sudden temperature changes. | Quick extreme shifts |
These tests show the board resists cracks and damage from heat changes. They prove the board works in tough places. Whether for factory machines or medical implants, rigid-flex PCBs are strong and reliable.
Rigid-flex PCB applications in industrial control
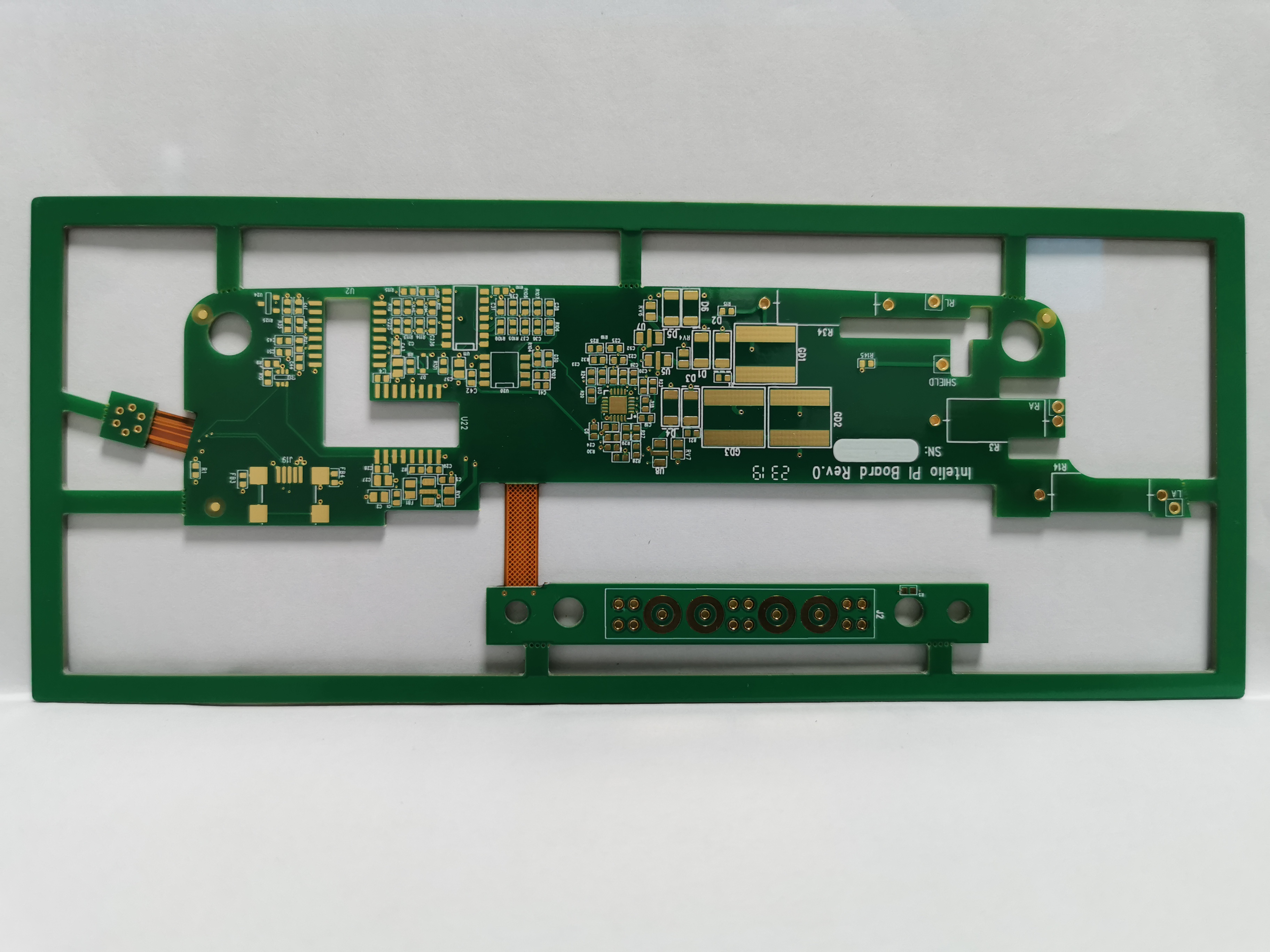
Robotics and automation systems
Robots and machines need small and accurate designs. Rigid-flex PCBs are perfect for this. They are strong and can bend, making them great for robot arms and moving parts. These boards save space and stay reliable in tight spots.
Automation also improves with rigid-flex PCBs. Machines can build these boards without mistakes. This makes production faster and better. Below are some benefits of rigid-flex PCBs for robots and automation:
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Helps make small and detailed designs that save space. | |
Flexibility | Combines bending ability with strength for complex electronics. |
Automation Integration | Machines build them well, reducing mistakes and improving quality. |
Control panels and sensors
Control panels and sensors use rigid-flex PCBs because they are small and tough. These boards handle shaking and heat changes without breaking. They are used in cars, planes, and medical tools where accuracy matters.
For example, rigid-flex PCBs make phones and tablets thinner. They also make car dashboards and sensors strong and dependable. Below are examples of their uses:
Application Area | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Saves space and handles stress well | Compact assemblies | |
Medical | Makes small and flexible tools like implants and sensors | Better comfort for patients |
Automotive | Resists shaking and heat changes | Dashboards, sensor networks |
Consumer Electronics | Helps make thin devices like phones and tablets | Smartphones, tablets, laptops |
Equipment for harsh environments
Factories and other tough places need strong equipment. Rigid-flex PCBs work well in heat, shaking, and wet conditions. They keep working in places like oil rigs and airplanes.
Manufacturers test these boards to make sure they last. Heat tests check for weak spots in solder joints. Shaking tests make sure parts stay in place. Below are some testing methods:
Testing Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
Finds weak solder joints and checks if parts expand correctly in heat. | |
Vibration Testing | Tests if parts stay secure during shaking or transport. |
Humidity and Corrosion Testing | Checks if coatings protect against water damage and long-term wear. |
Rigid-flex PCBs help equipment stay strong and reliable in tough places.
Rigid-flex PCB uses in medical devices
Wearable medical devices
Wearable medical tools have changed healthcare. They help track health all the time. Rigid-flex PCBs are important because they are small and bendable. Engineers use them to make light and comfy devices that fit the body. These boards are great for fitness trackers, heart monitors, and glucose testers.
Rigid-flex PCBs are strong and flexible. This keeps devices working well for a long time. For example, a heart monitor must handle movement and still give correct readings. These boards remove the need for big connectors. This makes devices smaller and lighter. People can wear them easily every day.
Imaging and diagnostic systems
Medical imaging tools need to be exact and dependable. Rigid-flex PCBs are used in MRI machines, CT scanners, and X-rays. These boards bend to fit tight spaces but still work well. They help parts talk to each other, which is key for accurate results.
Rigid-flex PCBs also make imaging tools stronger. They handle heat and stress found in hospitals. This is why they are used in patient monitors and lab machines. Their small size helps make portable imaging tools. Doctors can use these in faraway places.
Benefits of rigid-flex PCBs in imaging tools include:
Bending to fit tricky designs.
Working well in tough places.
Saving space for smaller machines.
These features make rigid-flex PCBs important for better imaging technology.
Surgical tools and medical implants
Surgical tools and implants need to be exact and strong. Rigid-flex PCBs are used in surgical robots, tiny instruments, and implants like pacemakers. These boards help make small and useful designs for medical tools.
For surgical robots, rigid-flex PCBs allow smooth movements and steady performance. This helps doctors do hard surgeries more accurately. For implants, these boards resist body fluids and temperature changes. This keeps them working for a long time.
Rigid-flex PCBs are also key for telemedicine tools. These tools help doctors check patients from far away. They need to be small and tough. Rigid-flex PCBs make sure telemedicine devices stay strong and useful.
Uses of rigid-flex PCBs in surgery and implants include:
Pacemakers and other implants.
Tiny surgical tools.
Telemedicine devices for remote care.
Rigid-flex PCBs help create new designs and keep devices reliable. They are changing medical technology for the better.
LT CIRCUIT’s skill in making rigid-flex PCBs
Smart designs for industrial systems
LT CIRCUIT makes top-notch rigid-flex PCBs for tough jobs. Their boards work well in hard conditions and handle tricky tasks. They use polyimide film, a strong material that resists heat. This helps machines run smoothly even in extreme heat or cold.
They also create multi-layer boards with tiny, accurate lines. These improve how machines like robots and car sensors work. The boards bend easily but still stay strong and reliable.
Some of their key ideas include:
Special materials like polyimide film to manage heat better.
Multi-layer boards with fine lines for better performance.
Reliable PCBs for medical tools
LT CIRCUIT makes rigid-flex PCBs perfect for medical devices. Their boards are small and bendable, great for wearables, scanners, and surgery tools.
These PCBs are built to handle tough medical needs. They resist heat changes and stress, so they work well in critical tools. Whether it’s a heart monitor or a surgery robot, their boards are precise and long-lasting.
Focused on quality and trust
Choosing LT CIRCUIT means getting dependable products. Their PCBs go through strict tests like heat and shake checks. This ensures they work perfectly in tough places.
Their attention to detail means every board meets high standards. This has made them a trusted name for industrial and medical PCBs. LT CIRCUIT’s boards are known for being reliable and innovative.
Rigid-flex PCBs have changed industrial and medical tools greatly. They are strong, bendable, and save space in designs. These boards work well even in tough conditions. LT CIRCUIT creates advanced boards, giving dependable solutions for hard tasks.
FAQ
What industries use rigid-flex PCBs the most?
Rigid-flex PCBs are common in medical tools, factory systems, airplanes, and cars. They are trusted because they are small and reliable.
How do rigid-flex PCBs make devices better?
These boards improve devices by having fewer connection points. This boosts signal quality and allows smaller designs for tough places like airplanes and cars.
Can rigid-flex PCBs handle tough conditions?
Yes, they can. Rigid-flex PCBs work well in heat, cold, shaking, and wet areas. This makes them great for airplanes and cars in hard environments.
See Also
Exploring The Structure And Function Of Rigid-Flex PCBs
Compact, Durable, Intelligent: The Benefits Of HDI Rigid-Flex PCBs
How Multilayer Rigid-Flex Circuit Boards Are Manufactured
Identifying The Right PCB For ATE Applications
Essential Steps For Multi-Impedance Control In PCB Manufacturing
