Key Differences Between Single-Layer and Multilayer PCBs in Industrial Settings
Industrial workers notice significant differences between single-layer and multilayer PCB solutions. While single-layer PCBs are cost-effective and straightforward, making them suitable for control systems and automotive applications, the multilayer PCB application has become standard in advanced industries. Multilayer PCB application allows for greater circuit density and enhanced performance, meeting the demands of modern technology. LT CIRCUIT offers both options to accommodate a wide range of requirements. Understanding these key differences in multilayer PCB application can impact project outcomes, costs, and overall efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Single-layer PCBs are simple and cheap. They are easy to repair. This makes them good for basic industrial jobs like control systems and sensors.
Multilayer PCBs work better and hold more parts in a small space. They can handle hard conditions. They are great for advanced electronics in telecom and medical devices.
Picking the right PCB depends on how hard your project is, your budget, and where you use it. Choosing well gives better results and saves money.
Single-Layer PCB
Structure
A single-layer pcb has a simple design. It has one copper layer on one side of the board. The board can be made from FR-4 fiberglass, aluminum, or CEM. Each material has different strength and heat features. A solder mask covers the copper to stop rust and shorts. On top, a silkscreen shows where parts go. The copper layer can be thick or thin, depending on use. Most single-layer pcbs are about 1.57mm thick. Some are as thin as 0.2mm or as thick as 6.1mm. Parts are put on the side without copper. There are no vias, so the design is easy. This makes building single-layer pcbs fast. LT CIRCUIT uses good materials and careful work to make strong single-layer pcbs for factories.
Benefits
Single-layer pcbs are cheap and easy to make. They need fewer parts and steps, so they cost less. The design is simple, which means fewer mistakes and faster work. It is easy to put together and fix because everything is on one side. This makes them last longer and break less often. Fewer layers mean fewer problems. They also get rid of heat well, especially with copper or aluminum. This helps in high-power uses. LT CIRCUIT checks every step to make sure the pcbs are good.
Industrial Uses
Single-layer pcbs are used in many factory jobs. They are found in control systems, small sensors, and relay boards. Cars use them for things like dashboard controls. Simple medical devices also use single-layer fpc. These jobs like single-layer pcbs because they save money and are easy to fix. They are made fast, so they are good for big orders with simple circuits. Workers can find and fix problems quickly. This makes single-layer fpc great for easy, high-volume designs. LT CIRCUIT gives strong single-layer fpc and pcb choices for factories.
Multi-Layer PCB
Structure
A multi-layer pcb has many copper layers stacked together. There is insulation between each copper layer. Makers pick materials like FR-4 or Rogers for different needs. The process starts with planning and getting materials ready. Each copper layer is shaped, cleaned, and pressed together. Machines help keep the layers lined up right. This makes the boards better. After pressing, the stack cools down slowly. This stops it from bending. Holes are drilled and filled to link the layers. This makes a strong multi-layer fpc. LT CIRCUIT follows strict rules to make sure each board is good.
Multi-Layer PCB Advantages
Multi-layer pcb has many good points. It can fit lots of parts in a small space. It keeps signals clear and spreads power well. These boards cut down on signal noise and handle heat. Designers can make small, complex circuits. This saves space and weight. Multi-layer fpc lets people design flexible circuits. It works for tough electronics. Multilayer pcbs work better and last longer. This makes them great for hard jobs. LT CIRCUIT uses new tech to make top multi-layer boards for factories.
Industrial Uses
Multilayer pcbs are used in many fields. Computers, phones, and factory machines need these boards. They work well and last a long time. Cars and medical tools use multi-layer pcb for small, strong, and cool-running designs. Multilayer pcbs are small but powerful. They help smart devices and machines do more. LT CIRCUIT makes custom multi-layer fpc and pcb for these jobs. This helps companies get strong and lasting boards.
Comparison
Cost
Aspect | Single-Layer PCBs | Multilayer PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Production Cost Difference | Cost increases 30-50% per additional layer | |
Manufacturing Complexity | Simpler, no lamination or via plating | Complex lamination, drilling, plating, inspection |
Yield Rates | Typically >99% for simple designs | Lower yields (85-92%) |
Cost Behavior by Volume | Cheaper at volumes <100 units | Cost-effectiveness improves above 1,000 units |
Hidden Costs | May require larger board sizes and external components | Higher rework and quality control costs |
Application Suitability | Simpler applications, cost-sensitive production | Complex, high-density, high-speed applications |
Single-layer PCB solutions are the cheapest to make. They use less material and take less time to build. Multilayer PCBs, even double-layer PCBs, cost more as you add layers. Using special materials and extra steps makes them pricier. When companies order a lot, multilayer PCBs can save money because of better designs. Still, single-layer PCBs are best for projects that need to save money.
Tip: Double-layer PCBs are a good choice if you want something between simple and complex.
Complexity
Factor | Single-Layer PCBs | Multi-Layer PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Design Complexity | Needed for complex circuits with many components | |
Space Constraints | Adequate for designs with enough surface area | Required when space is limited and high component density needed |
Manufacturing Steps | Simpler production process | More complex, including lamination and multi-layer stacking |
Repairability | Difficult to repair due to layer complexity |
Single-layer PCBs are easy to design. Engineers can draw paths and put parts on fast. Double-layer PCBs are a bit harder, since both sides are used. Multilayer PCBs are for very tricky circuits. They have stacked layers for lots of paths. These boards need skilled workers and careful building. Fixing problems is easier on single-layer and double-layer PCBs. Multilayer PCBs are harder to fix because the inside layers are hard to reach.
Double-layer PCBs give more ways to connect than single-layer.
Complicated gadgets often need multilayer PCBs to fit everything.
Performance
Multilayer PCBs work better for tough jobs. They have special ground and power layers to stop noise. This helps signals stay clear and move fast. Single-layer and double-layer PCBs cannot block noise as well. This makes it easier for signals to get mixed up in hard devices.
Double-layer PCBs help with routing but are not as strong as multilayer.
Multilayer PCBs use smart stacking to keep signals safe.
These things make multilayer PCBs the top pick for hard jobs like medical tools, car controls, and phones. Single-layer PCBs are fine for simple things that do not need much power.
Suitability
Feature/Aspect | Single-Layer PCB | Multilayer PCB |
|---|---|---|
Complexity | Complex circuits with high component density | |
Cost | Low manufacturing and design cost | Higher cost due to complex fabrication |
Production Speed | Longer lead times due to multiple layers | |
Troubleshooting | Easier visual inspection and repair | More difficult due to multiple layers and vias |
Thermal Management | Better for low-power, low-heat applications | Better heat dissipation for high-power applications |
Typical Industrial Uses | Consumer electronics, LED lighting, basic automotive electronics, prototyping, power supplies | Smartphones, medical devices, aerospace, telecommunications, advanced computing devices |
Single-layer PCBs are good for simple things like LED lights and home gadgets. Double-layer PCBs are used for things that are a little more tricky, like power supplies and basic factory controls. Multilayer PCBs are best for hard jobs that need to be small and work really well. Engineers pick the right PCB by looking at how hard the circuit is, how well it needs to work, how much it costs, and how easy it is to fix.
Note: Multilayer PCBs are better for advanced uses, but single-layer and double-layer PCBs are still important for cheap and easy-to-fix jobs.
Multilayer PCB Application
Industrial Sectors
Multilayer pcb application is very important in many industries. These industries need strong technology and reliable products. Some main areas use multi-layer boards the most:
Consumer electronics are the biggest users. Phones, tablets, laptops, and game consoles all need small, powerful multi-layer boards.
Car makers use multi-layer boards in electric cars, smart driving systems, and digital dashboards.
Medical electronics need multilayer pcbs for scans, implants, and portable monitors.
Factories use multi-layer boards for machine cameras, controllers, and smart meters.
Telecom companies use multilayer pcb application in 5G and network gear.
These areas help multilayer pcb application grow fast. Consumer electronics were worth $12.0 billion in 2023. They may reach $16.0 billion by 2032. Cars, factories, telecom, and medical devices are also growing. This shows more people want advanced pcb applications.
Industry | Application Example | Typical Layer Count | Benefits Highlighted |
|---|---|---|---|
Smartphones | 10-12 layers | High performance, reliability, compact design | |
Industrial Automation | Robotics | 6-10 layers | Reliability, harsh environment performance |
Telecommunications | 5G Base Stations | N/A | Signal integrity, noise reduction, reliability |
LT CIRCUIT Solutions
LT CIRCUIT makes special multilayer pcb application for every industry. Their engineers build multi-layer boards with 4 to 32 layers. They pick the right number of layers for each job. Customers can choose different finishes, solder mask colors, and built-in parts for small designs. LT CIRCUIT helps with stack-up, picking materials, and making the layout better. They use new tools like laser imaging and microvia drilling. This lets them make thin lines and close spaces.
Quality is very important at LT CIRCUIT. They use machines to check boards with cameras and X-rays. They follow world rules to make sure every multi-layer pcb is good. Fast samples and full tests help customers avoid problems and finish faster. LT CIRCUIT knows a lot about multi-layer boards. This helps telecom, factory, and electronics companies get strong, high-quality multilayer pcbs for hard jobs.
Tip: LT CIRCUIT’s multi-layer boards work well for tricky designs and give steady results in tough places.
Choosing the Right PCB
Project Needs
To pick the best PCB, you must know what your project needs. Engineers check how hard the circuit is, how big it can be, how strong it should be, and how well it must work. The table below shows how single-layer and multilayer PCBs fit different needs:
Project Need / Factor | Single-Layer PCB Characteristics | Multi-Layer PCB Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Functionality Complexity | Suitable for simpler, less complex circuits | Ideal for advanced, complex circuits requiring more connections |
Size Constraints | Larger size needed to add functionality | Smaller size due to stacking layers, fits more functionality |
Durability Requirements | Less durable, thinner boards | More durable, thicker boards withstand harsh industrial conditions |
Budget | Lower cost, simpler design and production | Higher cost due to complex design and manufacturing |
Lead Time | Shorter lead time, faster production | Longer lead time due to complexity |
Operation Frequency | Lower operating capacity and speed | Higher operating capacity and speed |
Circuit Density | Limited by single conductive layer | Higher density with multiple layers |
Repair Complexity | Easier to repair due to simplicity | More complex repairs due to hidden inner layers |
Reliability in Harsh Environments | Less reliable under harsh conditions | More reliable and suitable for harsh industrial environments |
How hard a project is helps decide which pcb to use. Easy jobs, like simple sensors or control panels, often use single-layer PCBs. These are cheap and easy to fix. Harder jobs, like factory controllers or smart electronics, need multilayer PCBs. These boards hold more circuits and work better. Flexible and rigid-flex PCBs are for special things, like wearables or medical tools, where space and bending matter. What the board is made of also depends on where and how it will be used.
Pick double-layer PCBs for medium-hard jobs.
Choose multilayer PCBs for very hard circuits.
Tip: Always pick the PCB that matches what your project needs now and later.
Budget
Money is important when picking the right pcb for factories. Single-layer PCBs are cheaper to make and design. They are good for big orders of simple things. Multilayer PCBs cost more because they use more stuff and need harder steps to build. The chart below shows how much different PCBs usually cost:
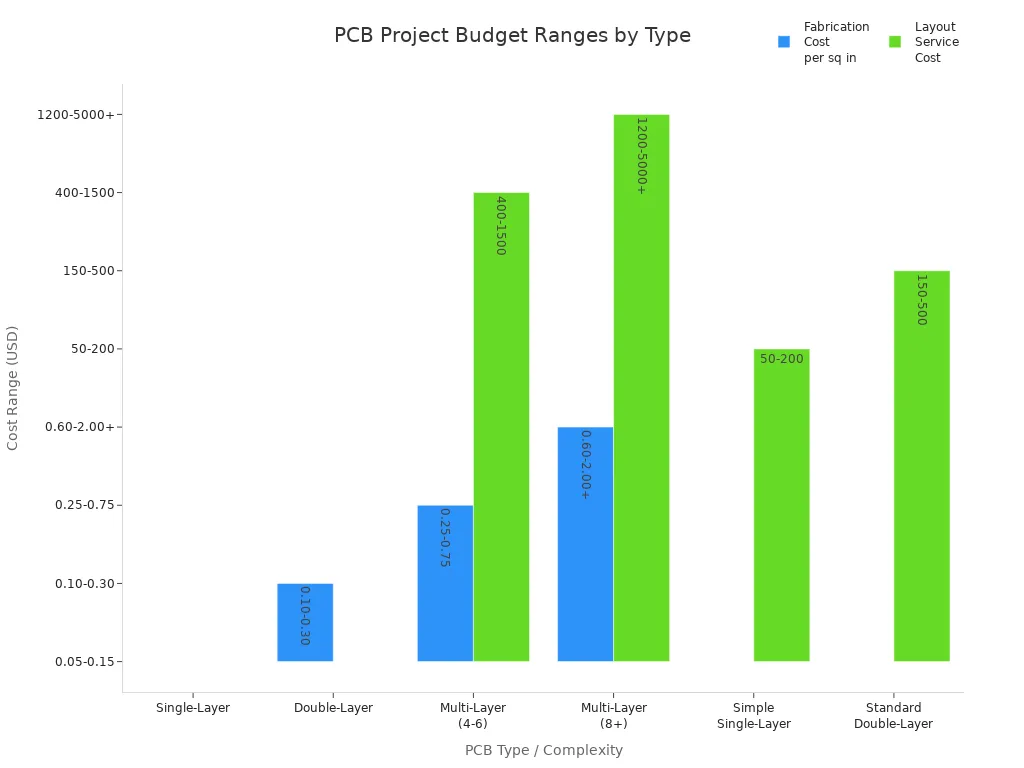
PCB Type | Complexity Level | Typical Cost Range (USD) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
Single-Layer | Lowest | $0.05 - $0.15 per square inch | Simple circuits, basic consumer electronics |
Double-Layer | Moderate | $0.10 - $0.30 per square inch | Basic industrial control, IoT |
Multi-Layer (4-6) | High | $0.25 - $0.75 per square inch | Advanced industrial control, complex electronics |
Multi-Layer (8+) | Very High | $0.60 - $2.00+ per square inch | High-speed digital, complex signal processing |
Single-layer PCB projects usually cost from tens to a few hundred dollars. Multilayer PCB jobs can cost thousands or even more, especially for big or high-tech uses. The price goes up if you use special materials, more layers, or extra features. If you order a lot, each board costs less, but the main things that change the price stay the same.
Note: You can save up to 25% on multilayer PCB costs by using fewer layers or making the design simpler, and still get good results.
Environment
Factories can be tough places for PCBs. They may face high heat, wet air, shaking, and strong signals. The right PCB must handle these things to keep working safely. Multilayer PCBs are thicker and use better materials, so they do better in hard places. They can take heat, pressure, and bumps, so they are good for planes, cars, and big machines.
Temperature: High-Tg FR-4 or polyimide boards can take heat up to 260°C.
Thermal Management: Heat sinks and thermal vias help stop hot spots.
Humidity: Special coatings keep out water and stop rust.
Vibration: Thicker boards and rigid-flex types soak up shocks and lower damage.
EMI: Good grounding, shields, and smart paths cut down on signal noise.
Rules help people pick the right materials and ways to build PCBs for tough places. Multilayer PCBs meet these rules for hard jobs, but single-layer PCBs are fine for easier places.
Callout: Always think about where the PCB will be used. Picking the right one helps it last longer and saves money on repairs.
PCB Type | Key Features & Best Use Cases |
|---|---|
Simple, low-cost, easy to fix; best for basic, budget-friendly factory projects. | |
Multilayer | Small, fits many parts, very reliable; great for advanced, high-performance factory uses. |
Picking the right PCB type helps save money and keeps things working well. Experts say you should choose makers who know what they are doing. LT CIRCUIT gives trusted quality, new technology, and special help for every factory job.
FAQ
What is the main difference between single-layer and multilayer PCBs?
Single-layer PCBs have just one copper layer. Multilayer PCBs have many copper layers stacked together. Multilayer PCBs are better for hard circuits and work faster in factories.
When should a company choose a multilayer PCB?
A company should pick a multilayer PCB for smart electronics or when lots of parts need to fit in a small space. Multilayer PCBs are best if you need strong signals and less noise in tough factory places.
Does LT CIRCUIT offer custom PCB solutions for unique industrial needs?
Yes, LT CIRCUIT makes special single-layer and multilayer PCBs for each job. Their engineers help pick the right materials, finishes, and designs for what each factory needs.
See Also
Exploring Diverse Industry Uses For Multilayer PCBs
Comparing Single, Double, And Multilayer PCB Types
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques For Heavy Copper Multilayer PCBs
Challenges In Prototyping And Manufacturing Multilayer Circuit Boards
