What Is a Multilayer Ceramic PCB and How Does It Work
A multilayer ceramic pcb features multiple layers of ceramic material stacked together, each layer embedded with copper circuits. This design results in a compact and highly durable printed circuit board. The multilayer ceramic pcb offers several advantages:
It efficiently dissipates heat and maintains stability even at temperatures exceeding 300 °C.
It supports high-frequency devices and allows for the integration of many layers within a limited space.
It provides excellent electrical insulation and exceptional mechanical strength.
LT CIRCUIT is at the forefront of innovative multilayer ceramic pcb technology.
Metric | Value (USD Billion) | CAGR (%) | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
Global ceramic-based PCB market | 9.8 | 2026-2033 | |
Projected market size | 5.8 (2033) |
Key Takeaways
Multilayer ceramic PCBs have layers of ceramic and copper stacked together. These boards are strong and can handle heat well. They can hold many parts in a small area.
These PCBs move heat away fast. They keep electrical signals clear. They last longer even in hard conditions. This makes them good for high-power and high-frequency devices.
Aerospace, automotive, and LED lighting industries use multilayer ceramic PCBs. They help devices work better and last longer. They also make devices more reliable.
Multilayer Ceramic PCB Structure
Ceramic Materials in Multilayer PCB
Ceramic materials are the base of every multilayer ceramic pcb. These materials give the pcb special features like good heat flow, strong insulation, and toughness. Engineers pick the ceramic type based on what the project needs. The most used ceramics in these pcbs are alumina, aluminum nitride, and beryllium oxide. Each one has its own benefits for building a multilayer ceramic pcb.
Ceramic Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Cost and Color | Key Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Alumina (Al2O3) | Lower cost, white color | Good thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, corrosion resistance | LEDs (3W-5W), general electronics | |
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | 150 - 320 | Higher cost, brown color | Superior thermal conductivity, good electrical insulation | High-power devices, heat-sensitive electronics |
Beryllium Oxide (BeO) | Very high | Requires special handling | Extremely high thermal conductivity, excellent heat dissipation | High-power RF amplifiers |
Alumina is used the most because it is not too expensive and works well. Aluminum nitride moves heat much better, so it is best for powerful or hot ceramic pcb jobs. Beryllium oxide moves heat the best, but it needs careful handling. The ceramic you choose changes how well the pcb moves heat and how long it lasts.
Ceramic multilayer pcb designs use these materials because they have high dielectric constants, do not expand much with heat, and resist chemicals. These features make ceramic pcb good for high-frequency, high-power, and tough jobs.
Layering and Circuit Design
A multilayer ceramic pcb has a special structure for better performance and strength. It has layers of ceramic and copper circuits stacked together. Makers get thin ceramic sheets ready and print copper lines using special methods. They stack the layers and join them with high heat.
1. Engineers pick good ceramic materials like alumina or aluminum nitride for their heat and electrical features. 2. They choose how many layers to use, usually from 4 to 20. 3. Each layer gets copper circuits printed on it to make paths for electricity. 4. Vias are made by laser or drilling to connect the layers. 5. The stack is heated below 1000 °C to bond the ceramic and copper. 6. This lets them put small parts inside the layers, so more parts fit. 7. A balanced stack-up keeps the board flat and strong. 8. Power and ground layers are close to stop signal problems. 9. Different via sizes are used for power, ground, and signals to help the board work better. 10. Solder masks and stencils help control solder and stop mistakes.
Good alignment and bonding are very important. This makes sure the ceramic multilayer pcb is strong and works right.
The way the signal, power, and ground layers are arranged, plus where the vias go, helps keep signals clear and heat under control. Using ceramics that move heat well and smart circuit design lets the multilayer ceramic pcb handle lots of power and fast signals. The multilayer setup also makes the board small but able to hold many parts, which is great for new technology.
LT CIRCUIT’s Expertise in Ceramic Multilayer PCB
LT CIRCUIT is a top company in making ceramic multilayer pcbs. They use new technology and follow strict rules to make sure their ceramic pcb products are high quality. LT CIRCUIT meets ISO 9001 and IPC standards, so every multilayer ceramic pcb is reliable.
LT CIRCUIT uses the latest tools like laser drilling, Laser Direct Imaging, vacuum reflow soldering, Automated Optical Inspection, and X-ray checks.
Their engineers plan each ceramic multilayer pcb carefully, thinking about the stack, heat, and signals.
LT CIRCUIT makes many types of ceramic pcb, including ones for high heat and multi-layer jobs in power electronics, LEDs, RF devices, and machines.
The team looks at things like space for parts, how boards are grouped, and edge design to make sure the boards are easy to build and last long.
LT CIRCUIT knows a lot about printed circuit technology, so they can add lots of circuits and special features for tough jobs.
The company’s focus on quality and new ideas makes them a trusted choice for businesses that need strong ceramic multilayer pcbs. LT CIRCUIT’s ceramic pcb products give great heat flow, strong insulation, and tough strength. These things help electronic devices work well and last longer.
How Multilayer Ceramic PCBs Work
Electrical and Thermal Performance
A multilayer ceramic pcb has a special structure. This structure helps it work better with electricity and heat. The board has many layers of ceramic and copper stacked together. This lets engineers put more circuits and parts in a small area. When parts are close, signals travel faster and paths are shorter.
The ceramic in the board keeps signals clear at high speeds. This means signals do not get mixed up or lost.
Metal film layers have low resistance. This helps signals move easily and makes the board work better.
Ceramic moves heat away from hot spots very fast. This keeps the board cool and safe when it is working.
The board’s design lets engineers arrange layers in smart ways. They can place power, ground, and signal layers to stop interference and keep signals strong.
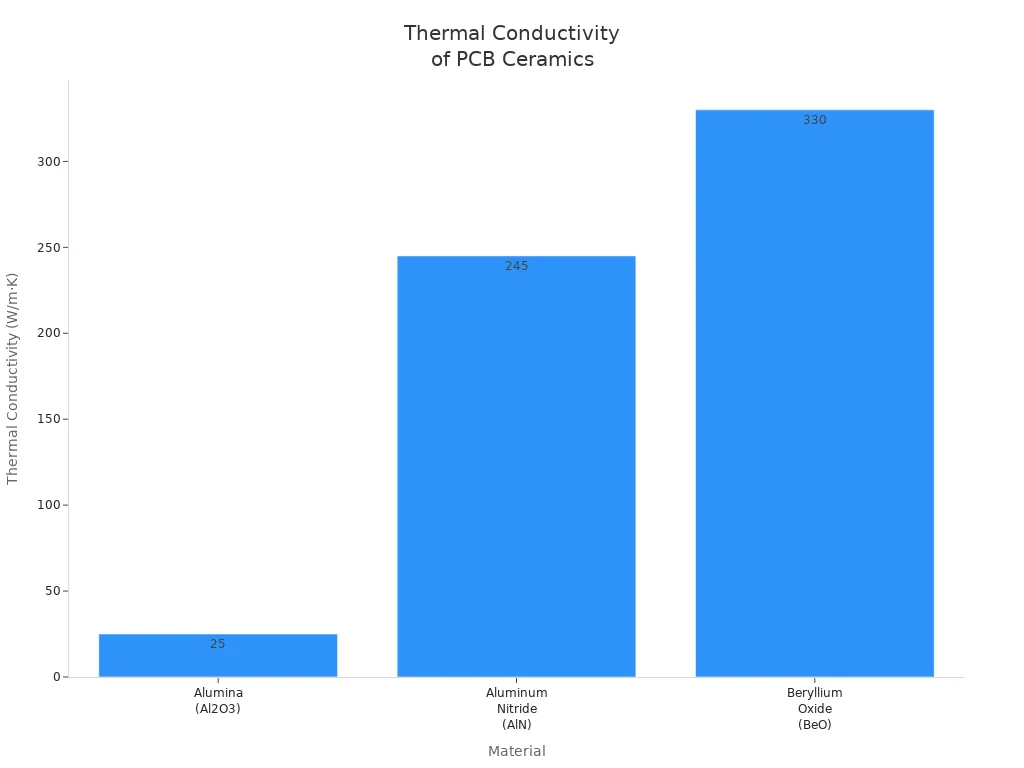
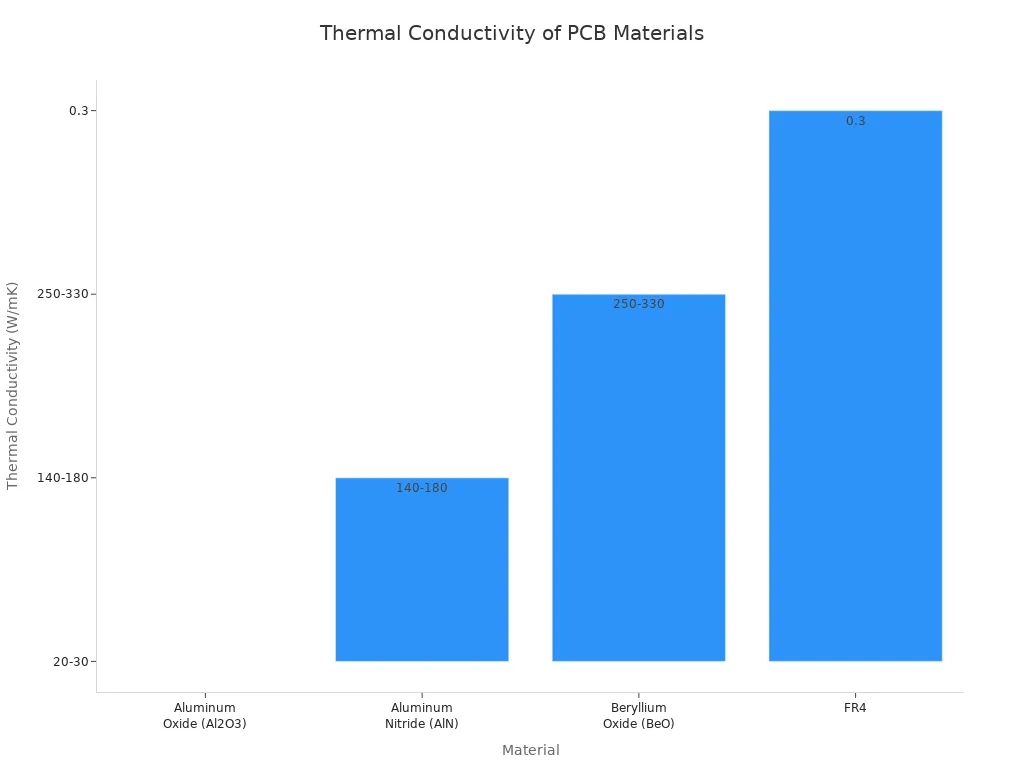
The table below shows how well ceramic pcb materials move heat compared to FR4 pcbs:
Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|
Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) | |
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | 140 to 180 |
Beryllium Oxide (BeO) | 250 to 330 |
FR4 | Around 0.3 |
Ceramic pcb materials move heat much better than FR4. Some ceramics move heat up to 100 times better. This is very important for devices that need to stay cool and work well.
A multilayer ceramic pcb also keeps electricity inside and is very strong. The ceramic layers do not bend or break easily. This helps the board last longer, even in tough places. Because of these features, multilayer ceramic pcbs are great for powerful and fast devices.
Manufacturing Process Overview
Making a ceramic pcb takes many careful steps. Each step is important to make sure the board works well.
First, ceramic powders and binders are mixed to make a paste. The paste is spread into thin sheets. These sheets are heated to remove extra stuff and make them strong.
Next, metal paste is printed on the ceramic sheets. The sheets are fired at high heat to stick the metal to the ceramic.
Then, photoresist and UV light are used to draw the circuit paths. Chemicals remove extra metal, leaving only the needed circuits.
After that, the layers are stacked and lined up. Holes called vias are drilled to connect the layers. The stack is fired again to join everything together.
A top metal layer, like copper or gold, is added. This helps the board carry electricity and makes it easier to solder parts.
At the end, the board is checked and tested. Engineers look for problems and test the board to make sure it works right.
LT CIRCUIT uses special tools like laser drills and X-ray checks. They follow strict rules to make sure every board is good. They use ISO 9001 and IPC standards to keep quality high.
Cross-section analysis lets engineers find hidden problems. This step helps make sure the board will last a long time.
Applications of Multilayer PCB
Ceramic pcb technology is used in many industries. These boards are needed where strong performance and reliability matter most. Multilayer ceramic pcbs are used when heat, insulation, and strength are very important.
Industry | Primary Application Examples | Key Details and Properties |
|---|---|---|
Satellite communication modules, radar systems | Operate in extreme temperatures; use aluminum nitride or silicon carbide; low dielectric loss for high-frequency signals | |
Automotive Electronics | EV charging stations, battery management, motor control units | Handle high currents; maintain low temperature rise; withstand vibrations and thermal cycling |
Industrial and Power Electronics | Solar inverters, motor drives | Support high voltages; ensure low junction temperatures; improve reliability in harsh environments |
Military and Defense | Missile guidance systems, ruggedized communication devices | Operate at very high temperatures; maintain signal integrity under vibration and chemical exposure |
LED Lighting and High-Power Semiconductors | Automotive headlights, industrial lighting | Efficient heat dissipation; extend LED lifespan |
These boards are used in cars, planes, factories, and more. In cars, they handle lots of power and heat. In planes, they work well in very hot or cold places and send signals fast.
LT CIRCUIT makes many types of ceramic pcbs for these jobs. Their boards help customers get better performance and longer life for their devices. Using a multilayer ceramic pcb means better heat control, strong signals, and more parts in a small space.
A multilayer ceramic pcb has layers of ceramic and copper. This makes the pcb strong and dependable. These ceramic pcb designs move heat away quickly. They also stop electricity from leaking. They can hold many layers for complex circuits.
Some main benefits of ceramic pcb are:
They get rid of heat fast and keep working well.
They fit lots of parts in a small space for new electronics.
They do not get damaged easily by tough conditions.
LT CIRCUIT gives good ceramic pcb options for any multilayer ceramic pcb job.
FAQ
What makes a multilayer ceramic pcb different from a standard printed circuit board?
A multilayer ceramic pcb has ceramic layers. These layers help move heat away fast. They also help electricity flow better. Most standard boards use FR4. FR4 does not move heat as well as ceramic.
Why do high-frequency devices use ceramic multilayer pcbs?
Ceramic multilayer pcbs are good for high-frequency devices. The ceramic keeps signals strong and clear. It stops signals from getting weak or mixed up. This helps the device work better.
What are common applications of ceramic multilayer pcbs?
Engineers use ceramic multilayer pcbs in many fields. They are used in aerospace, cars, LED lights, and power electronics. These jobs need good heat control and strong insulation.
See Also
A Step-By-Step Guide To Manufacturing Multilayer Ceramic PCBs
Understanding Multilayer PCBs And Their Role In Modern Devices
An In-Depth Look At The Manufacturing Process Of Multilayer PCBs
Comparing Single, Double, And Multilayer PCBs: Key Differences
Exploring The Diverse Industrial Uses Of Multilayer PCBs Today
